Project
Project Page
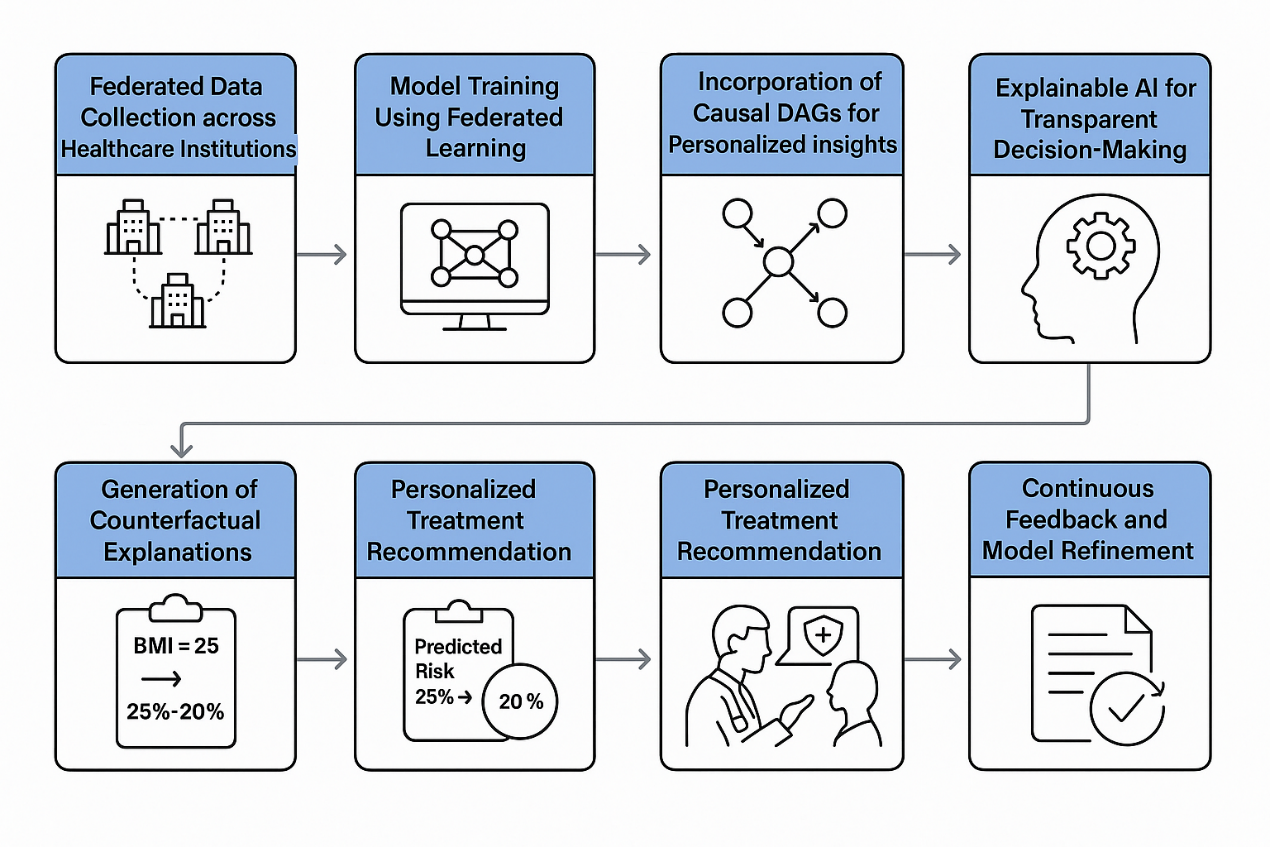
Personalised Treatment Planning in Healthcare
Personalised treatment planning in healthcare refers to the development of medical strategies that are specifically tailored to an individual’s unique characteristics, including their genetic profile, lifestyle, environment, and medical history. This patient-centric approach aims to enhance the effectiveness of treatments while reducing the risk of adverse effects. By promoting proactive prevention, active patient engagement, and collaborative decision-making between healthcare providers and patients, personalised treatment planning contributes significantly to improved clinical outcomes and overall well-being.
Dr. S. N. Tripathy
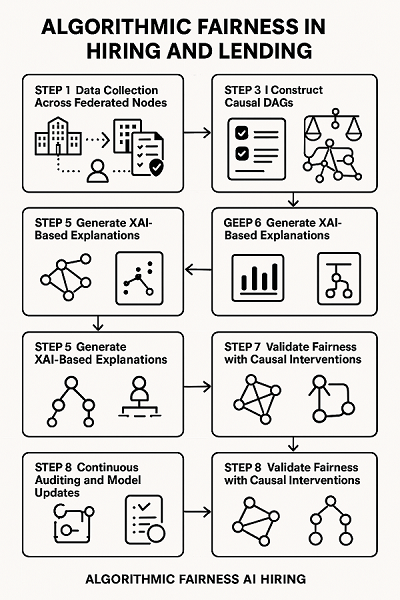
Algorithmic Fairness in Hiring and Lending
Algorithmic fairness plays a crucial role in ensuring unbiased and objective decision-making, particularly in domains such as human resources and financial services. In hiring processes, algorithms can be designed to identify and evaluate relevant skills and qualifications that align with job requirements, thereby promoting merit-based selection and reducing human bias. Similarly, in lending scenarios, fair algorithms support equitable loan approval decisions by assessing applicants based on consistent, transparent criteria. Applications of such fairness-focused algorithms extend to areas like employee recruitment, credit risk assessment, and even player selection in competitive environments.
Dr. S. N. Tripathy
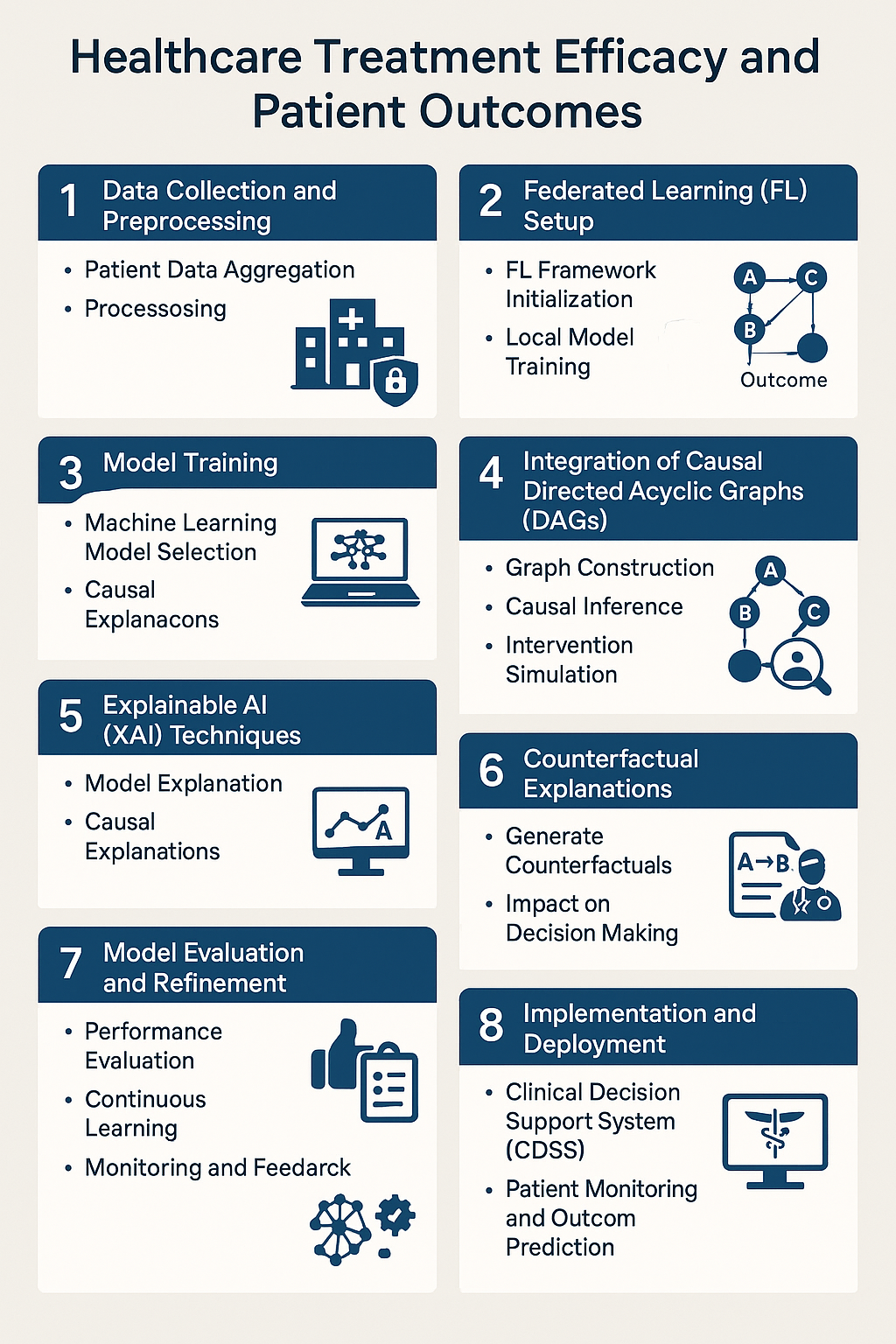
Healthcare Treatment Efficacy and Patient Outcomes
Improving patient outcomes is a critical objective, involving a comprehensive approach that includes enhancing overall health, promoting recovery, and preventing adverse events. Achieving these outcomes requires effective hospital administration, data-driven decision-making, and active patient engagement, all of which play vital roles in optimizing healthcare delivery and ensuring better patient care.
Dr. S. N. Tripathy
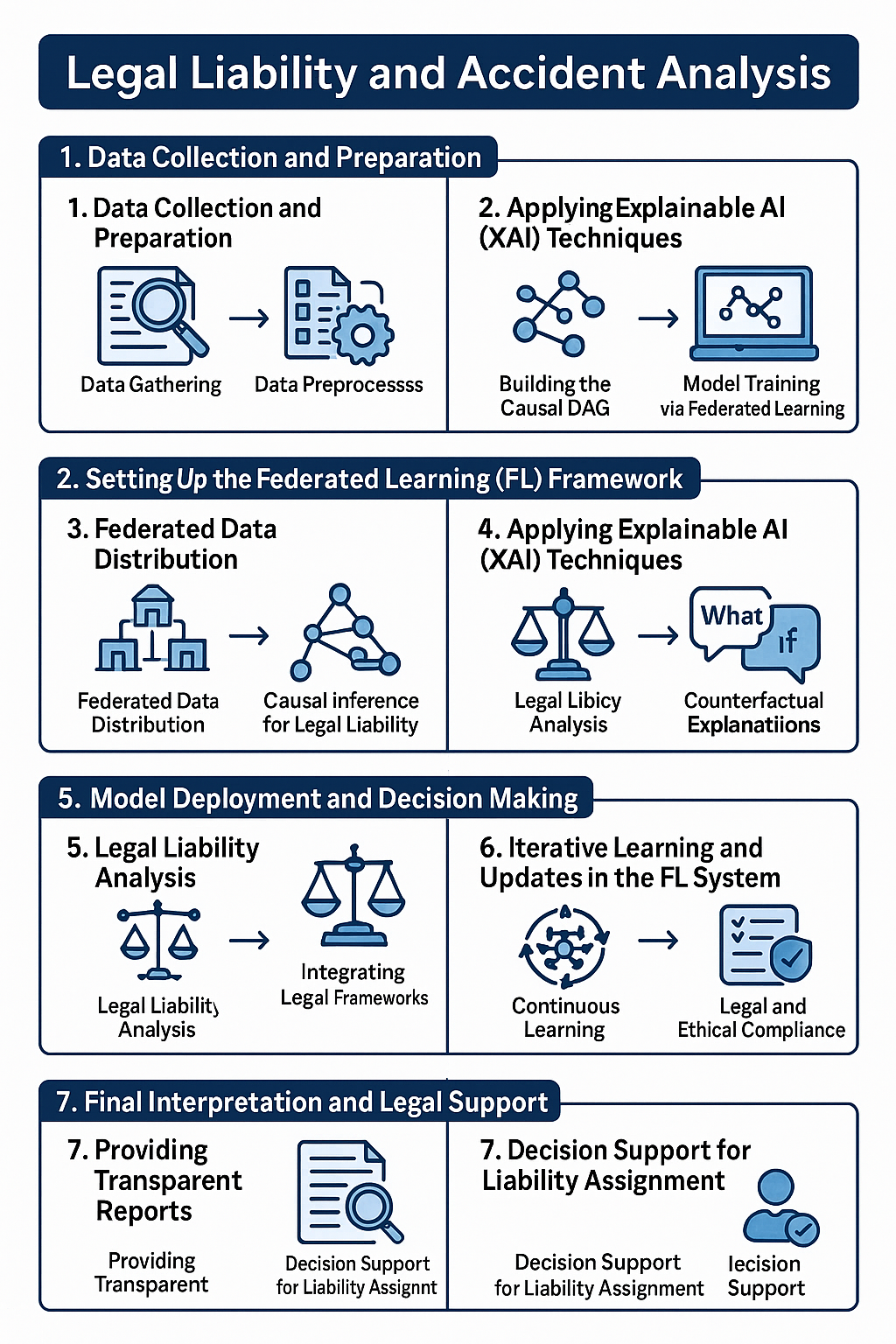
Legal Liability and Accident Analysis
Legal liability in the context of accidents refers to the determination of responsibility for compensating victims for harm resulting from an accident. It involves assessing when an individual or entity is legally obligated to provide compensation based on the circumstances of the incident. Accident analysis, on the other hand, focuses on investigating the causes and contributing factors of accidents to identify their root causes. This analysis is essential for implementing preventive measures and ensuring compliance with relevant legal and regulatory requirements. Legal liability is typically established through various legal doctrines, such as negligence, strict liability, and product liability, each applicable depending on the specifics of the accident and its context.
Dr. S. N. Tripathy
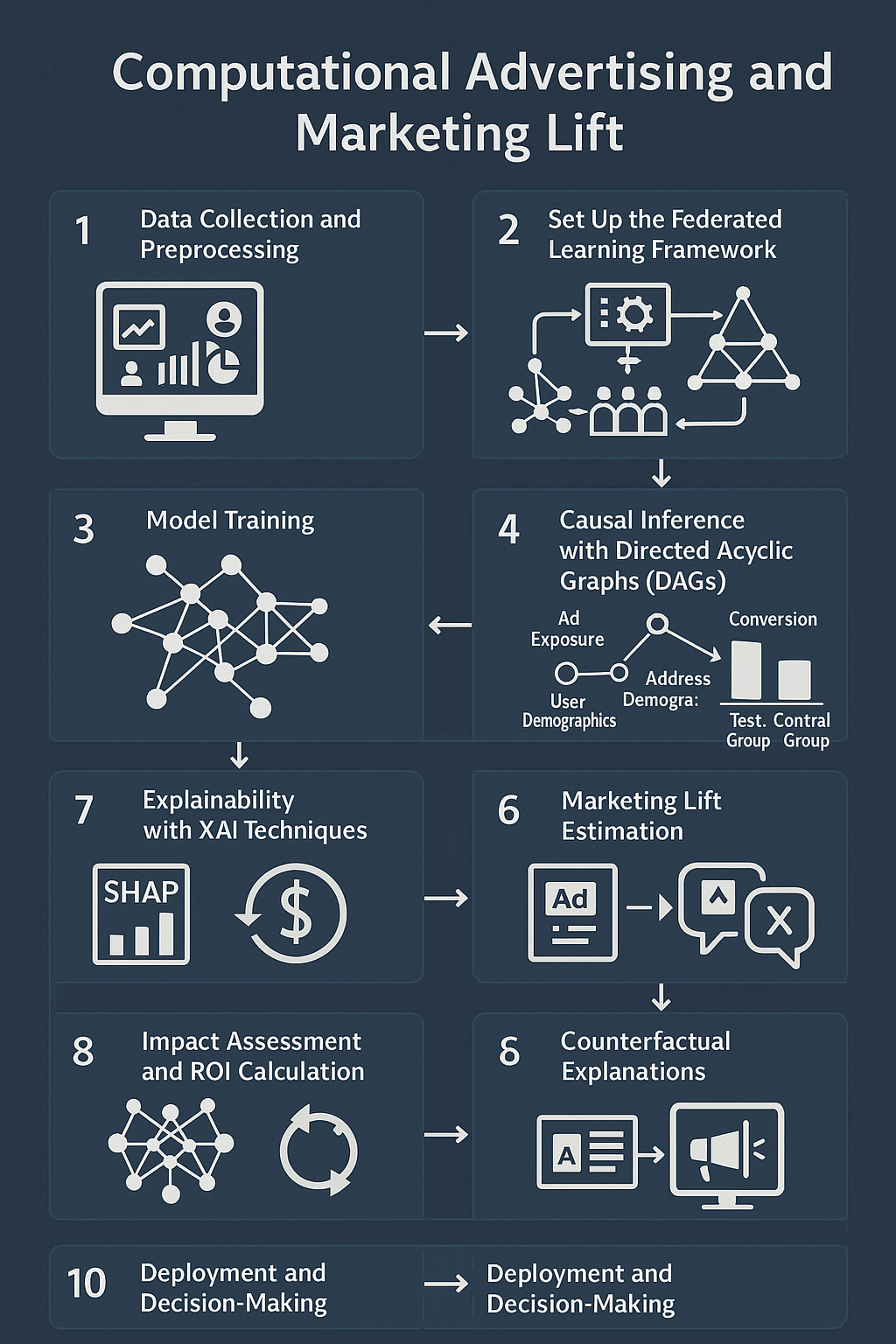
Computational Advertising and Marketing Lift
Computational advertising utilizes advanced algorithms to automate and optimize the delivery of advertisements, ensuring targeted and efficient outreach. Marketing lift analysis, on the other hand, evaluates the specific impact of marketing initiatives on key performance indicators such as conversions or revenue. This analysis determines whether a campaign or action has a measurable effect on customer behavior by comparing a test group exposed to the campaign with a control group. Causal effect estimators predict the sales outcomes had the ads not been shown, providing a precise assessment of the return on investment (ROI) for digital advertising campaigns.
Dr. S. N. Tripathy
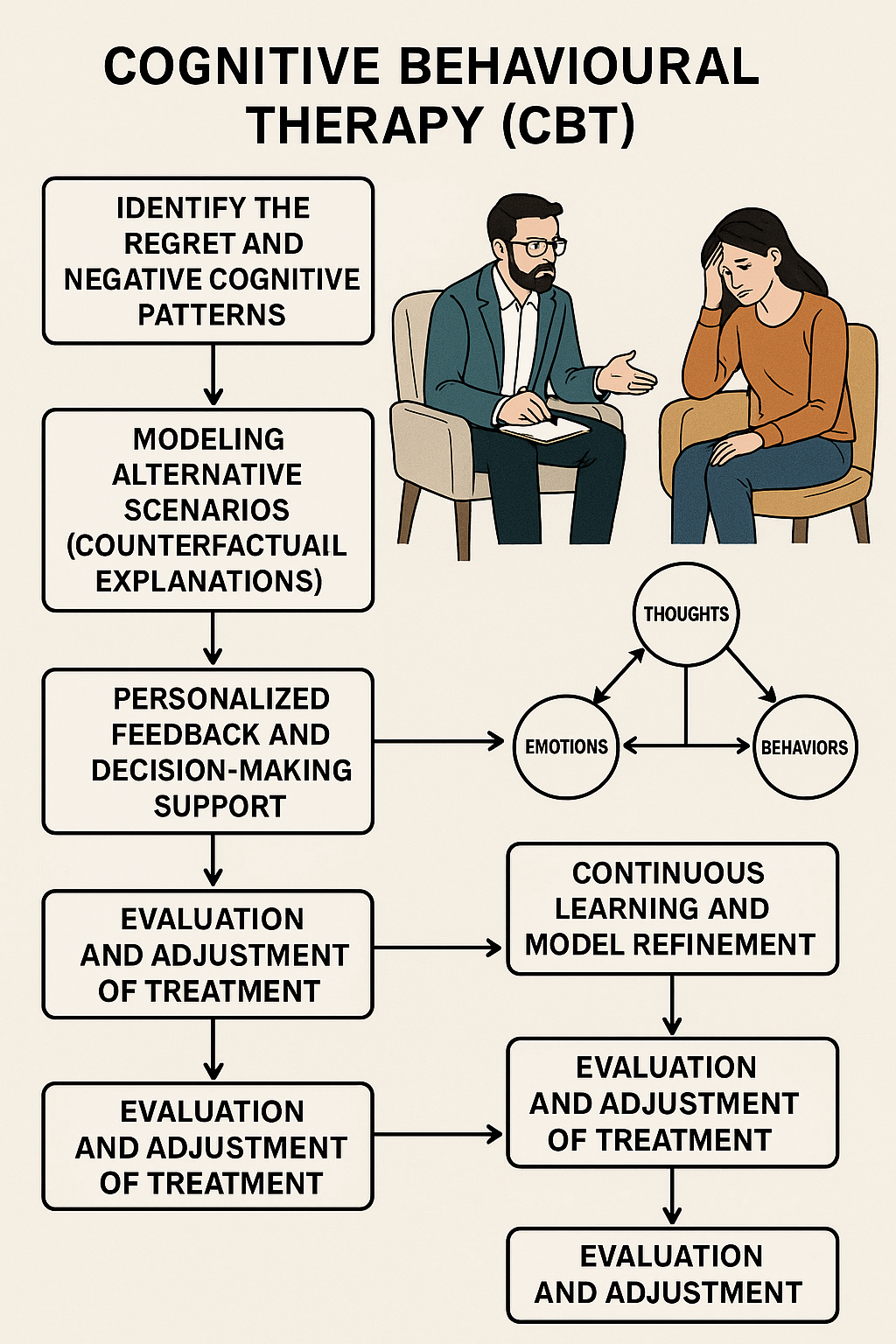
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) effectively mitigates regret by offering strategies to address and manage unhealthy thought patterns and emotions, fostering more positive outcomes. This therapeutic approach involves identifying and modifying negative thought processes related to past events and actions, ultimately reducing the intensity and emotional impact of regret. Additionally, other therapeutic modalities, such as Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT), can also play a significant role in managing and coping with regret.
Dr. S. N. Tripathy
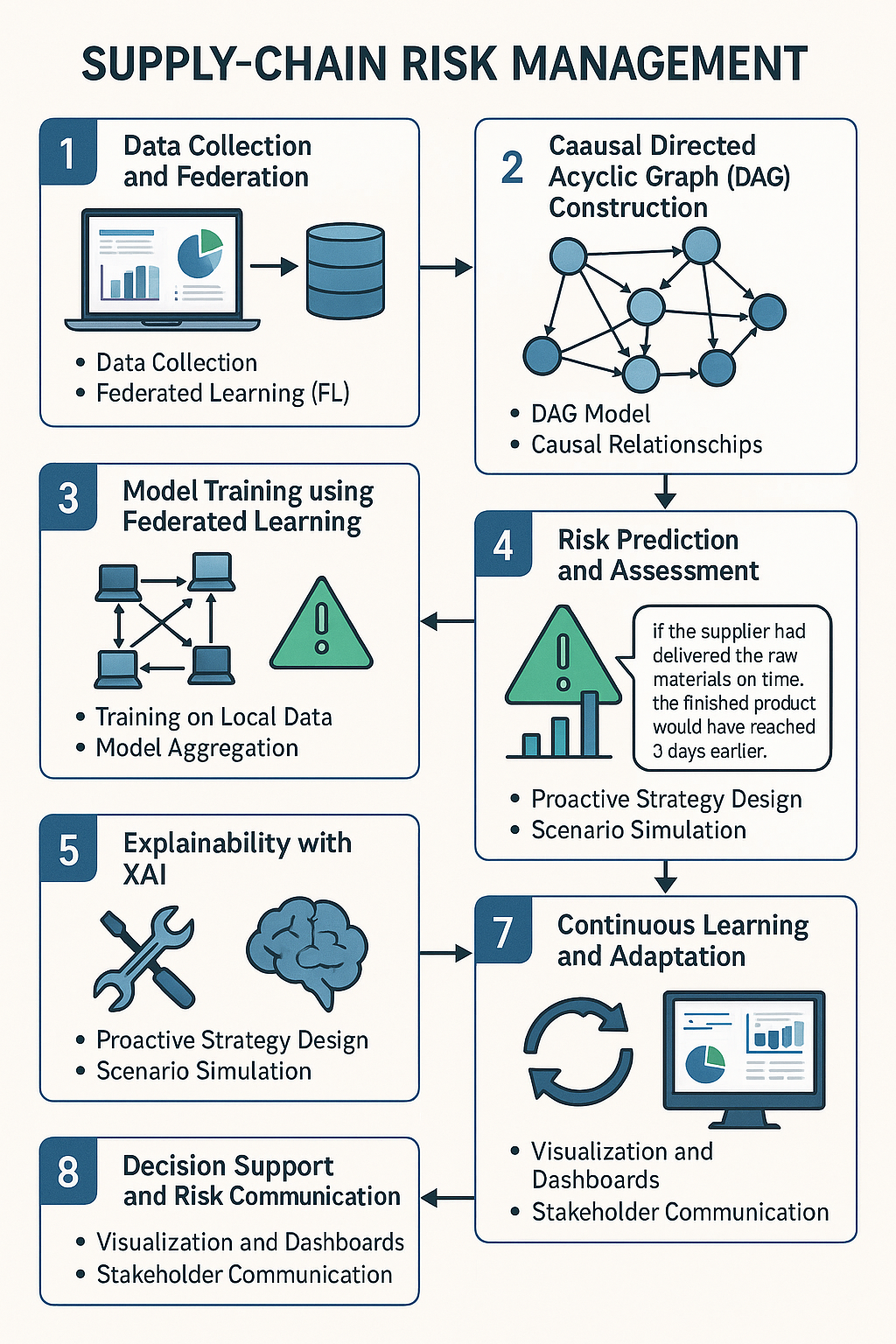
Supply-Chain Risk Management
Supply Chain Risk Management (SCRM) focuses on identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks across the entire supply chain, from raw material sourcing to the delivery of finished products. This includes evaluating risks related to suppliers, logistics, and distribution networks. The primary objective of SCRM is to ensure business continuity, safeguard profitability, and protect against potential disruptions. By analyzing factors such as supplier delays or port closures, SCRM helps identify key risks that could lead to order disruptions, enabling the implementation of proactive mitigation strategies to minimize impact.
Dr. S. N. Tripathy
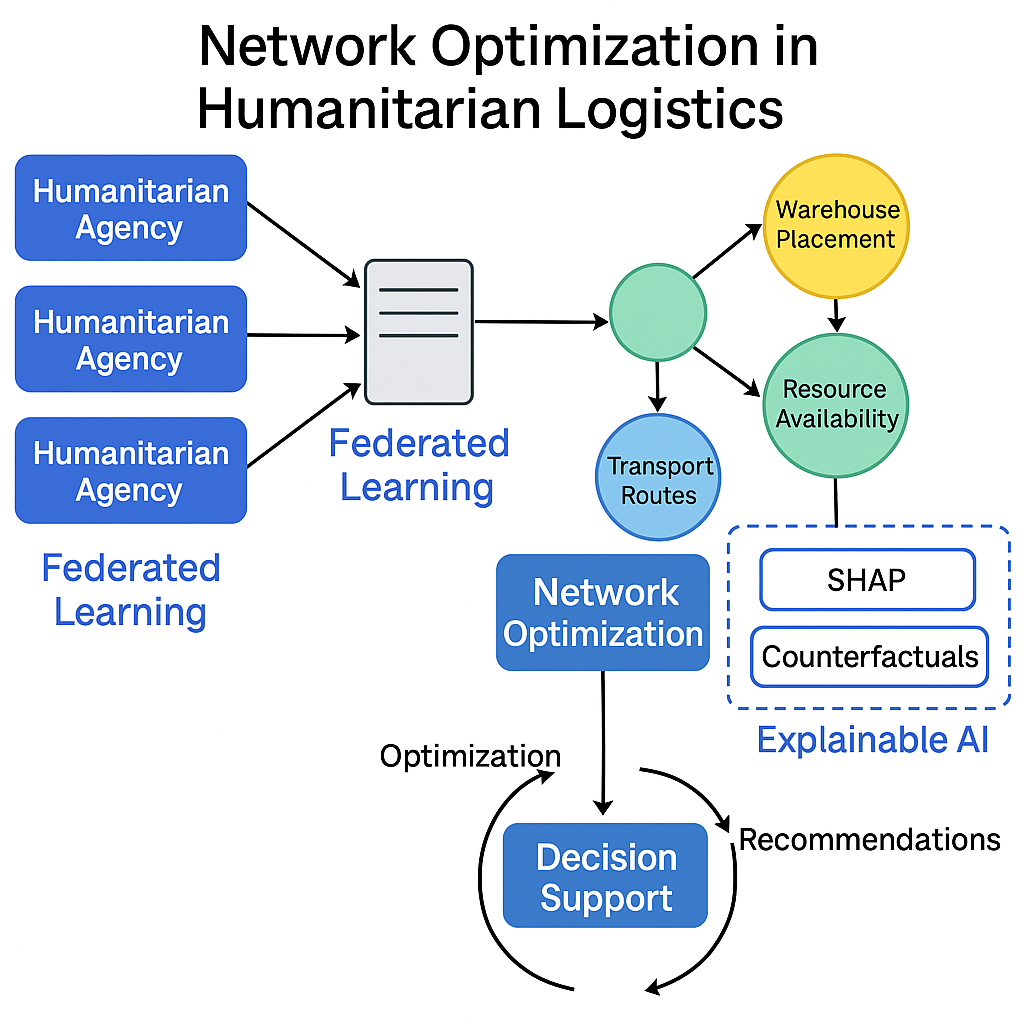
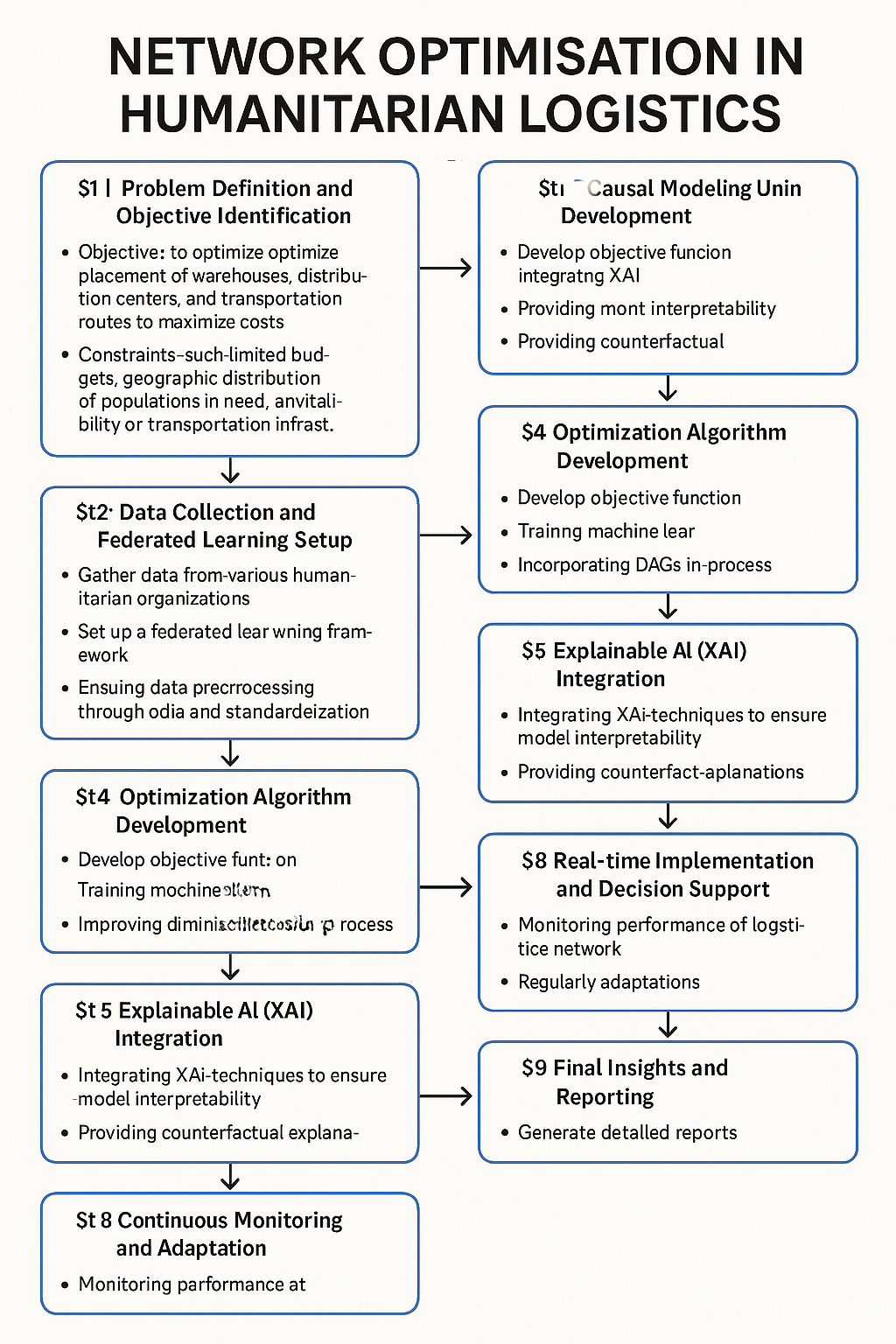
Network Optimisation in Humanitarian Logistics
This approach aims to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of aid delivery by optimizing the placement and movement of resources. It involves determining the most strategic locations for warehouses, distribution centers, and other facilities, as well as optimizing the allocation of resources and transportation routes to maximize the impact of relief efforts. The focus is on minimizing costs associated with facility setup, while providing clear justifications for decisions related to facility locations and operations within humanitarian relief efforts.
Dr. S. N. Tripathy
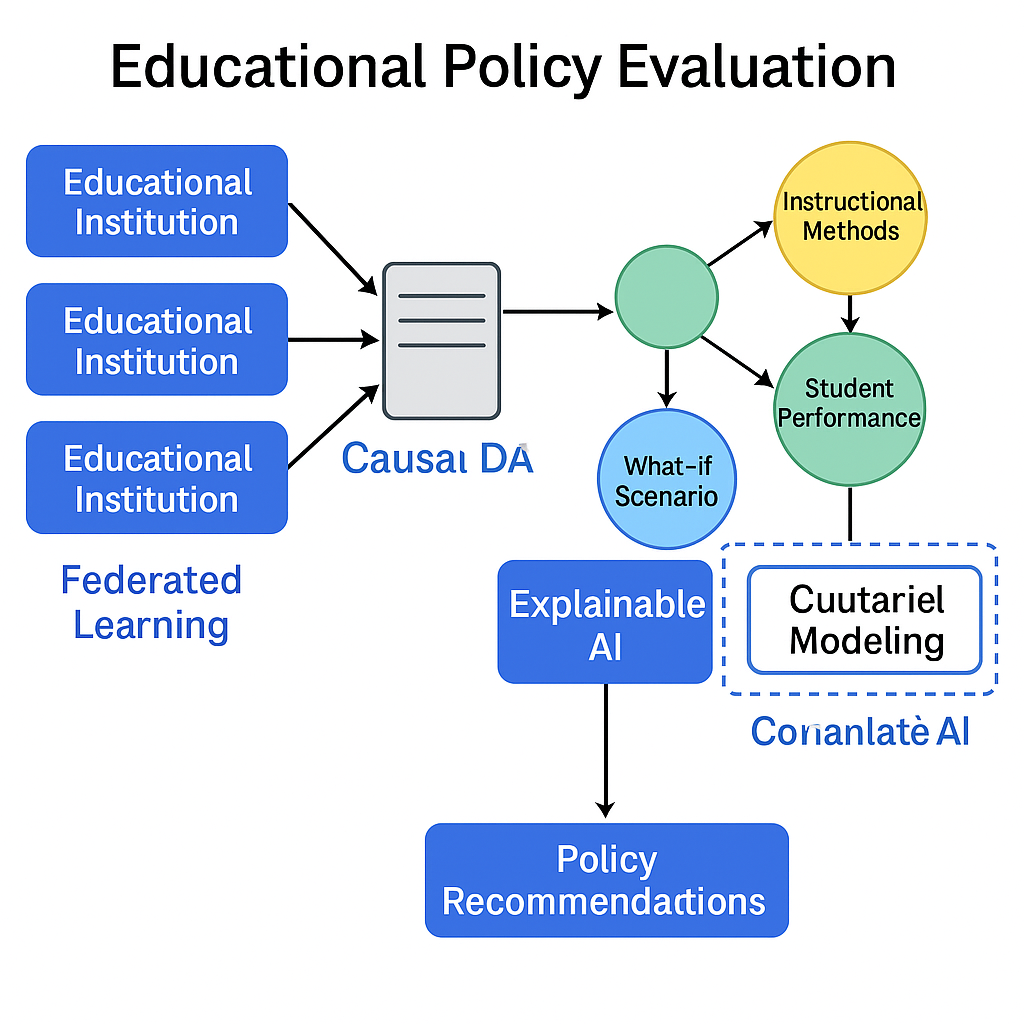
Educational Policy Evaluation
Educational policy evaluation involves the systematic collection and analysis of data to assess whether a policy is meeting its intended objectives, identifying any unintended consequences, and guiding future policy decisions. This process can be carried out throughout the entire policy cycle, from the initial design phase to implementation and subsequent stages. Counterfactual models are used to estimate how student performance would change under different curricula, providing valuable insights for adaptive learning and resource allocation in educational institutions. By determining which instructional methods and resources have a causal impact on student performance, these evaluations contribute to the optimization of adaptive learning systems.
Dr. S. N. Tripathy
Public Health Program Evaluation
Public Health Program Evaluation is a structured process aimed at assessing the effectiveness, efficiency, and impact of public health interventions. This process involves the systematic collection, analysis, and interpretation of data to determine the success of interventions, identify areas for improvement, and ensure that program objectives are being met. The primary goal is to enhance program quality and outcomes, while also providing accountability and justifying the allocation of continued funding.
Dr. S. N. Tripathy